multi-layer PCB
High-end design,
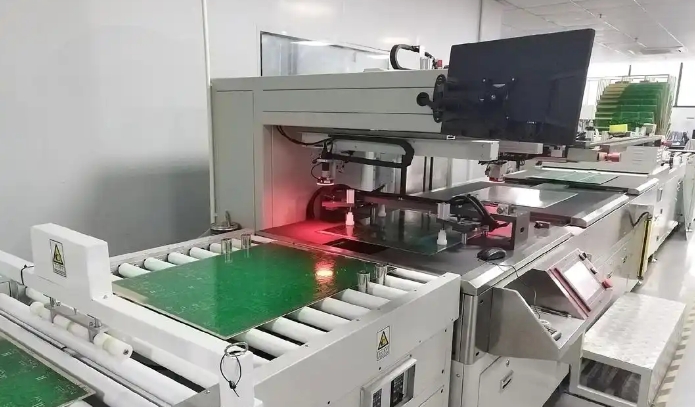
Read MoreHXPCB is a professional PCB industry supplier. We provide PCB manufacturing and assembly, and provide free proofing services for 2-6 layers of PCB. We provide one-stop production and assembly services such as double-sided PCB, multi-layer PCB, aluminum-based PCB, rigid-flex PCB, HDI PCB, UAV PCB, high-frequency PCB, etc. We have strong production equipment and technical team, which provides us with high-quality products at a more favorable price.





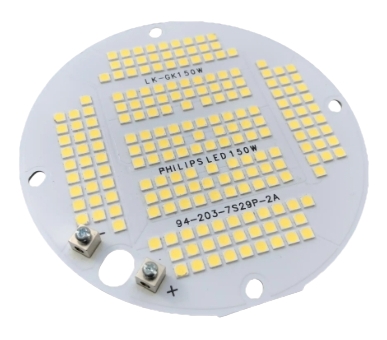
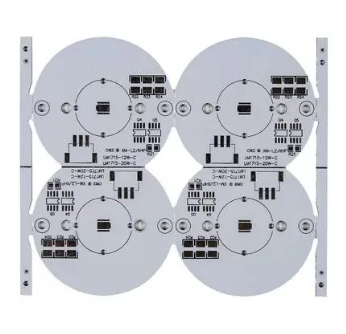

The full name of Aluminum PCB is Aluminum-based Printed Circuit Board. Generally speaking, it refers to a printed circuit board that uses aluminum as the base material. It consists of a copper conductive layer, an insulating layer (usually polyimide or other thermally conductive resins), and an aluminum metal base layer. Compared with traditional FR-4 substrates, aluminum-based PCBs have excellent thermal conductivity and can effectively dissipate heat, so they are very suitable for applications with high power and high heat dissipation requirements.
1. Excellent thermal conductivity
The aluminum material of aluminum-based PCB has a high thermal conductivity (about 180 W/m·K), which can efficiently disperse the heat generated by electronic components and prevent overheating from affecting the circuit. Its heat dissipation performance is much better than that of traditional FR-4 PCB, and is widely used in high-power devices that require heat dissipation.
2. Structural composition
2.1 Copper layer: responsible for the conduction and wiring of the circuit.
2.2 Insulation layer: usually polyimide (PI) or other high thermal conductivity resins are used, which plays a dual role of electrical insulation and thermal conductivity.
2.3 Aluminum base layer: as a substrate, it provides support and heat conduction.
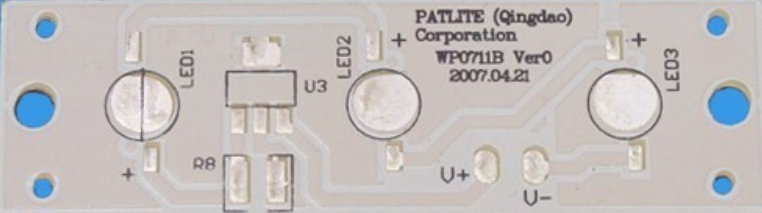
3. Application field
Aluminum PCBs are usually used in electronic equipment that requires high heat dissipation capabilities, such as LED lighting, power electronics, automotive electronics, communication equipment and industrial equipment. Especially in the LED industry, aluminum-based PCBs can effectively reduce the temperature of LED lamps and extend their service life.
4. Mechanical strength
Aluminum-based PCBs not only have superior thermal performance, but also strong mechanical strength, and can maintain stable electrical performance under harsh environmental conditions.
HXPCB is a PCB manufacturer with more than ten years of experience, providing customers with high-performance and high-quality circuit board solutions.
The company is able to respond quickly and provide small batch production and prototyping services to accelerate product development cycles. Through strict quality control and multiple tests, the quality and performance of each PCB are ensured.
HXPCB is committed to providing customers with customized PCB solutions, meeting the needs of different industries with efficient production processes and competitive prices.
1. Material selection and lamination process
The core advantage of aluminum-based PCB is its excellent thermal conductivity, but in the production process, how to select suitable materials and optimize the lamination process is a challenge. The lamination temperature, pressure and time need to be precisely controlled.
2. Thermal management design
The design needs to reasonably plan heat dissipation designs such as thermal vias, copper heat dissipation layers (copper pour), and thermal vias.
How to achieve more efficient heat conduction and heat dissipation on PCB also tests the experience of designers.
3. Combination of aluminum substrate and copper layer
How to ensure the mechanical combination between materials while maintaining good electrical performance is an important technical challenge in aluminum-based PCB design.
4. Circuit design and routing
Designers need to balance current carrying capacity and heat dissipation requirements and accurately calculate the routing width.
5. Processing and manufacturing accuracy
The production equipment of aluminum-based PCB must have high precision, and the processing technology needs to be very mature.
6. Environmental resistance and long-term stability
The materials and production processes of aluminum substrates need to have corrosion resistance and good mechanical strength to ensure that no failures occur during long-term work. In addition, the electrical performance of aluminum-based PCBs may be affected in hot and humid environments, so the reasonable selection of insulation layer and surface protection layer is also crucial.
Material Selection
The first step is to select the appropriate aluminum metal substrate material, which is chosen for its excellent thermal conductivity. The dielectric layer is usually made of a thermally conductive resin, such as polyimide, to provide electrical insulation while facilitating heat dissipation. The copper layer responsible for the circuit’s conductive path is also selected based on the design specifications.
Copper Cladding
The aluminum substrate is first covered with a thin copper foil, usually using a lamination process. This copper layer forms the circuit path, and the thickness of the copper foil is selected based on the current-carrying requirements of the final product. In some cases, copper deposition can be performed using electroplating methods to achieve more precise thickness control.
Drilling
After copper plating, the board is drilled according to the design specifications. Drilling is used to make through-holes (for heat dissipation and inter-layer connections) and to mount components. The drilling process must be carefully controlled to avoid damaging the aluminum substrate or the copper layer. When using precision drills, care must be taken to remove any burrs or debris generated during the drilling process to prevent short circuits.
Etching
The next step is the etching process, which removes excess copper from the surface, leaving the desired circuit pattern. This is usually done using a chemical etching process using an acidic or alkaline solution. The etching process must be carefully monitored to ensure that the copper paths are accurate and etched evenly, especially in areas with complex circuit designs.
Dielectric Lamination
Next a dielectric layer is applied to provide electrical insulation between the copper and aluminum layers. This layer is typically made of a thermally conductive material, such as polyimide or other engineering resins, which is laminated to the copper layer under controlled conditions of heat and pressure, ensuring a strong bond without damaging the delicate copper traces.
Surface Finishing
Surface finishes such as electroplating or gold plating are used to improve the solderability and conductivity of the board. This process is critical to ensuring PCB reliability, especially for high-power applications where high currents flow through the board.
Solder Mask Application
Solder mask is used to protect the copper circuits from oxidation and ensure that components are only soldered to the correct pads. Solder mask also prevents shorts between tracks with larger spacing.
Component Mounting and Assembly
Once basic PCB fabrication is complete, components are mounted on the board using either surface mount technology (SMT) or through-hole mounting techniques, depending on the design. Components are soldered to the board using either reflow or wave soldering processes.
Testing and Inspection
After assembly, the PCBs undergo rigorous testing and inspection. This includes electrical testing to check for shorts, opens, and proper operation, as well as visual inspection (including automated optical inspection, or AOI) to ensure that solder joints are correct and free of manufacturing defects.
Final Quality Control
Finally, the PCBs undergo a final quality control inspection, including an X-ray inspection of internal vias and layer junctions, to ensure that the board meets all design specifications and quality standards.
| Aluminum Substrate | Provides excellent thermal conductivity, typically made from 6061 or 5052 aluminum alloy. |
| Dielectric Layer | Commonly made from polyimide (PI) or epoxy resin for electrical insulation. |
| Conductive Layer | Copper is used for the conductive layer, typically in thicknesses of 1 oz/ft² or 2 oz/ft². |
| Solder Mask | A protective layer applied to prevent short circuits and corrosion, commonly available in green. |
| Surface Finish | Finishes like ENIG or HASL for enhanced solderability and protection. |
| Adhesives | Used to bond different layers in multilayer PCBs. |
| Thermal Interface Materials | Improve thermal conductivity for high-power components. |

Used in high-performance LED lighting systems to improve thermal management.
Used in power supply units and converters to achieve efficient heat dissipation.
Used in automotive lighting and control modules to ensure durability and reliability.

Used in RF and microwave components to provide efficient thermal conductivity.

Used in diagnostic and therapeutic equipment due to stringent reliability requirements.

Improved performance and thermal management in devices such as smartphones and tablets.

Used in machinery and automation systems to achieve optimal performance under high power conditions.
In devices such as smartphones and communication modules to improve performance and thermal efficiency.
| Parameter | Description |
| Base Material | Aluminum substrate (commonly 6061 or 5052 aluminum alloy) |
| Dielectric Material | Typically made of polyimide (PI) or epoxy resin for insulation |
| Thermal Conductivity | Generally greater than 1.0 W/m·K (often between 2-4 W/m·K) |
| Operating Temperature Range | Typically from -40°C to +150°C |
| Copper Thickness | Commonly 1 oz/ft² or 2 oz/ft², depending on current demands |
| Layer Count | Available in single-sided, double-sided, or multilayer configurations |
| Surface Finish | Options include ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), and immersion silver |
| Solder Mask | Typically available in various colors, with green being most common |
| Maximum Current Carrying Capacity | Generally higher due to improved thermal management |
| Mechanical Strength | Durable and suitable for harsh environments |
| Applications | Widely used in LEDs, power electronics, automotive applications, telecommunication devices, and medical equipment |
| Parameter | Aluminum PCB | Standard PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Aluminum substrate with dielectric layer | FR-4 (epoxy glass cloth), CEM-1, CEM-3, etc. |
| Thermal Conductivity | > 1.0 W/m·K (usually between 2-4 W/m·K) | < 0.5 W/m·K |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +150°C | -40°C to +130°C |
| Maximum Current Carrying Capacity | Typically higher, affected by copper thickness | Dependent on copper thickness, usually 1 oz/ft² or 2 oz/ft² |
| Heat Dissipation | Excellent, suitable for high-power applications | Relatively poor, suitable for standard power applications |
| Mechanical Strength | Strong and durable, suitable for harsh environments | Good, but generally lower toughness compared to aluminum PCB |
| Manufacturing Cost | Higher, especially in low-volume production | Lower, suitable for mass production |
| Solderability | Good, with attention to solder mask process |
| Parameter | Aluminum PCB Materials | Standard PCB Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate | Aluminum substrate (6061 or 5052 aluminum alloy) | FR-4 (epoxy glass cloth), CEM-1, CEM-3 |
| Insulation Material | Polyimide (PI), epoxy resin | Epoxy resin (such as Class B, Class C) |
| Conductive Material | Copper (typically 1 oz-2 oz thick) | Copper (typically 1 oz-2 oz thick) |
| Solder Mask | Photo-sensitive solder mask | Photo-sensitive solder mask |
| Surface Finish | ENIG, HASL, gold immersion, etc. | HASL, ENIG, etc. |
With more than ten years of experience and technical accumulation, HXPCB has become a trusted partner for customers. We provide aluminum-based PCB assembly services from prototype design to mass production. Whether it is high-frequency communication, data center, high-performance computing (HPC) or AI system, our professional team can easily solve it.
Choosing HXPCB is not only choosing advanced manufacturing technology, but also choosing a professional team to escort you throughout the process. We are committed to providing customers with efficient, reliable and customized aluminum-based board assembly solutions.
For more information about aluminum-based PCB assembly, please click PCB assembly or click XDCPCBA
Aluminum PCBs have a higher thermal conductivity, allowing for effective heat dissipation, making them suitable for high-power applications. Standard PCBs typically use FR-4 material, which has lower thermal performance, suitable for standard power applications.
Aluminum PCBs are widely used in LED lighting, power electronics, automotive electronics, medical devices, and telecommunications equipment, especially in high-heat scenarios.
The operating temperature of Aluminum PCBs typically ranges from -40°C to +150°C, depending on the materials and design choices.
Aluminum PCBs are primarily composed of an aluminum substrate, a dielectric layer (often polyimide or epoxy resin), and a copper layer.
Aluminum PCBs provide excellent heat dissipation through their aluminum substrate, effectively reducing the operating temperature of components and enhancing overall reliability.
Aluminum PCBs require careful solder mask processing, and they can typically be soldered using lead-free solder, showing good solderability.
The production cost of Aluminum PCBs is generally higher, especially in low-volume manufacturing, but it can decrease with mass production.
The copper thickness is usually based on the design's current density requirements, with common choices being 1 oz/ft² or 2 oz/ft².
Aluminum PCBs have high mechanical strength, able to withstand significant external pressure, making them suitable for high temperatures and harsh environments.
Common surface finishes include ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), and immersion silver, with choices depending on application requirements and cost considerations.


